

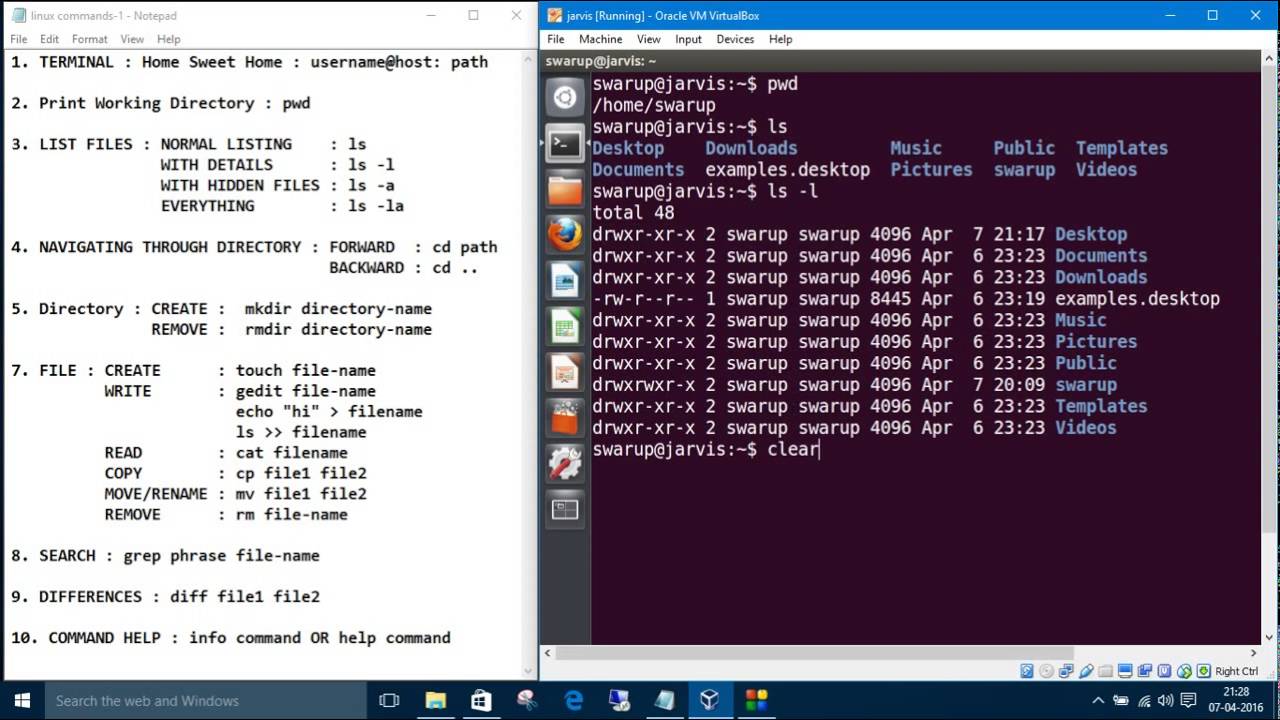
We use this information to complete transactions, fulfill orders, communicate with individuals placing orders or visiting the online store, and for related purposes. Online Storeįor orders and purchases placed through our online store on this site, we collect order details, name, institution name and address (if applicable), email address, phone number, shipping and billing addresses, credit/debit card information, shipping options and any instructions. We use this information to address the inquiry and respond to the question. To conduct business and deliver products and services, Pearson collects and uses personal information in several ways in connection with this site, including: Questions and Inquiriesįor inquiries and questions, we collect the inquiry or question, together with name, contact details (email address, phone number and mailing address) and any other additional information voluntarily submitted to us through a Contact Us form or an email. Please note that other Pearson websites and online products and services have their own separate privacy policies. This privacy notice provides an overview of our commitment to privacy and describes how we collect, protect, use and share personal information collected through this site. Pearson Education, Inc., 221 River Street, Hoboken, New Jersey 07030, (Pearson) presents this site to provide information about products and services that can be purchased through this site. The echo command prints all matching filenames in alphabetical order, butĭoes not format the listing in columns. mnt /opt /proc /root /sbin /tmp /usr /var bin /boot /dev /etc /home /lib /lost+found In order to list directories and files, specify a wildcard on the ThisĬommand, built in to each shell, is also a program found under the /binĭirectory. The echo command can also be used to list the contents of directories. Echoing Directory Contents with the echo Command
LINUX LIST DIRECTORY CONTENTS TO TEXT FILE MANUAL
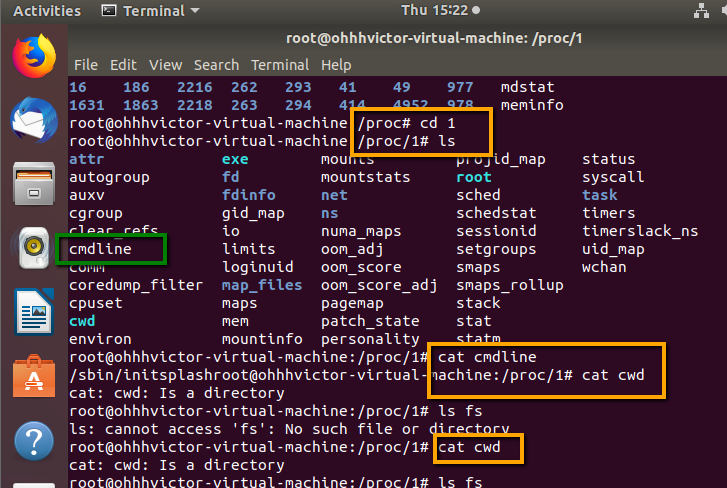
The manual pages for related directory listing commands, such as dir, vdir,
The ls command is documented in its manual page.
LINUX LIST DIRECTORY CONTENTS TO TEXT FILE HOW TO
To learn how to customize which colors are used for certain files, If you plan to make anĪlias for this, it's preferable to use ls -color=auto which will onlyĬolorize output sent to your screen (and not confuse programs you are piping For instance, by default all the subdirectories will be blue,Įxecutables will be green, text files will be white. You can use ls -color to easily distinguish file types in a directory Identify directories, links, and executablesĬhanging file and directory listing colors
List all files (including those beginning with. Long format listing (includes file size, dates, permissions, and so on) List directory names, not directory contents Table 3.1 lists some common command-line options that you can use to viewĭirectory contents in different formats. (/) and asterisk (*) to file or directory names: $ ls -F /usr/local/lib/* Option identifies directories and executable files by appending a forward slash View directory contents in different formats.
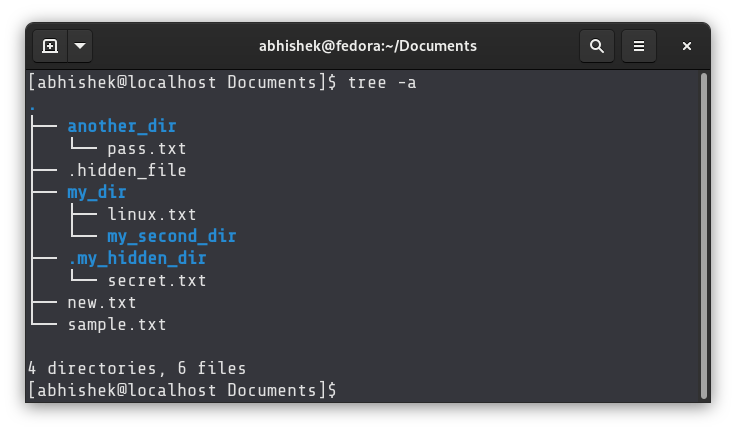
You can use different command-line options and wildcards to To list the contents of the /usr/local/ directory, typeīy default, the ls command lists the contents of directories in columns, Wildcards can be used to specify certainįiles or directories. This command has more than 40 different command-line options thatĬan be combined to format listings. Use the ls (list directory) command to list the contents of one or severalĭirectories. Listing Directories and Files with the ls Command The following sections describe severalĭirectory listing programs that are usually included with most Linuxĭistributions. Listing the contents of directories, like navigating through your system, isĪ basic skill you should quickly master.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
